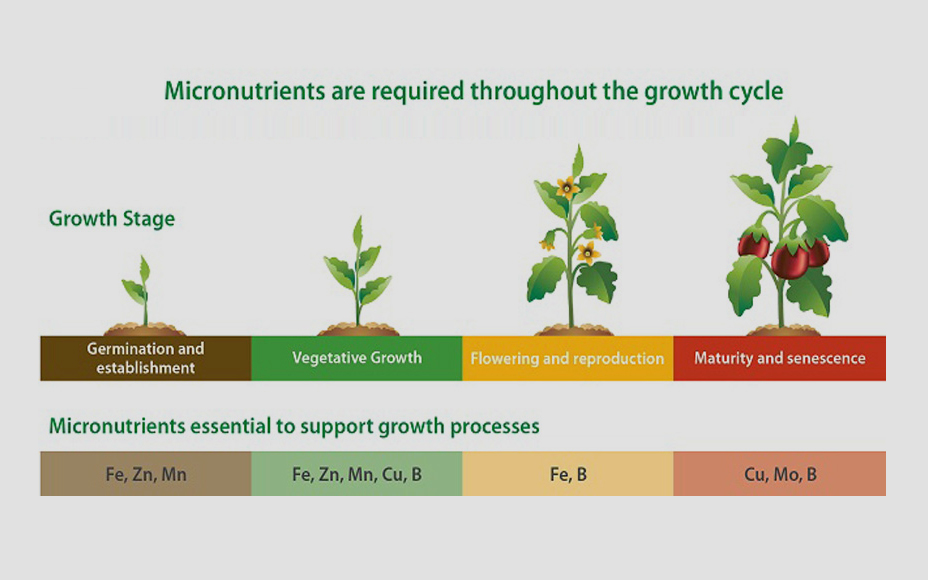
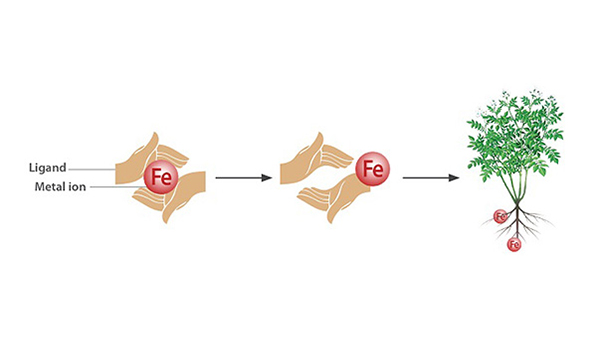
The Mechanism of Chelates
Chelate is a complex of a micronutrient ion and an organic molecule that "holds" it, called ligand. As long as the ion is attached to the ligand, it is protected from interacting with other ions in the solution, which might turn it unavailable for plant uptake.
As the Chelates micronutrient ions are consumed by the plant, more ions are released from the holding ligands, thus becoming available for plant uptake.This mechanism maximizes the efficiency of the micro nutrients applied. When maxEEma CMN is applied, the chelates ensure availability of micronutrients in both alkaline and acidic soils.